New PNAS editorial authored by a group of interdisciplinary experts is a byproduct of a retreat convened by APPC, NAS, & the Annenberg Foundation Trust at Sunnylands.


New PNAS editorial authored by a group of interdisciplinary experts is a byproduct of a retreat convened by APPC, NAS, & the Annenberg Foundation Trust at Sunnylands.

APPC hosted the annual SEJ conference April 3-7, focusing on Democracy, Disinformation, Activism… What’s Environmental Journalism’s Role?”

The Annenberg Public Policy Center celebrated its 30th anniversary by honoring the work of its former postdoctoral and FactCheck.org fellows and opening a new Climate Communication division.

As part of its 30th anniversary celebration, the Annenberg Public Policy Center has opened a new area of research, the Climate Communication division, led by Annenberg School for Communication vice dean Emily Falk.

Confidence in science remains high but has declined in the past few years, with just 42% saying scientists can overcome their biases.

In JAMA, 3 Penn scholars advocate for renaming of the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) and improving public understanding of the vaccine surveillance system.
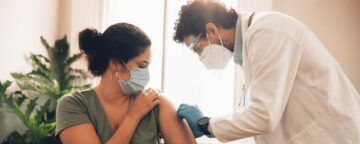
A new study from Annenberg researchers explores social norms around vaccination and how vaccination rates can be shaped by state laws and policies.

FactCheck.org has rounded up a dozen of the year's false and misleading claims, including remarks by President Joe Biden, former President Donald Trump, and presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr.