Showing people a "mental model" of scientific concepts may help undercut vaccine-related misconceptions, according to new APPC research published in PNAS.

Showing people a "mental model" of scientific concepts may help undercut vaccine-related misconceptions, according to new APPC research published in PNAS.
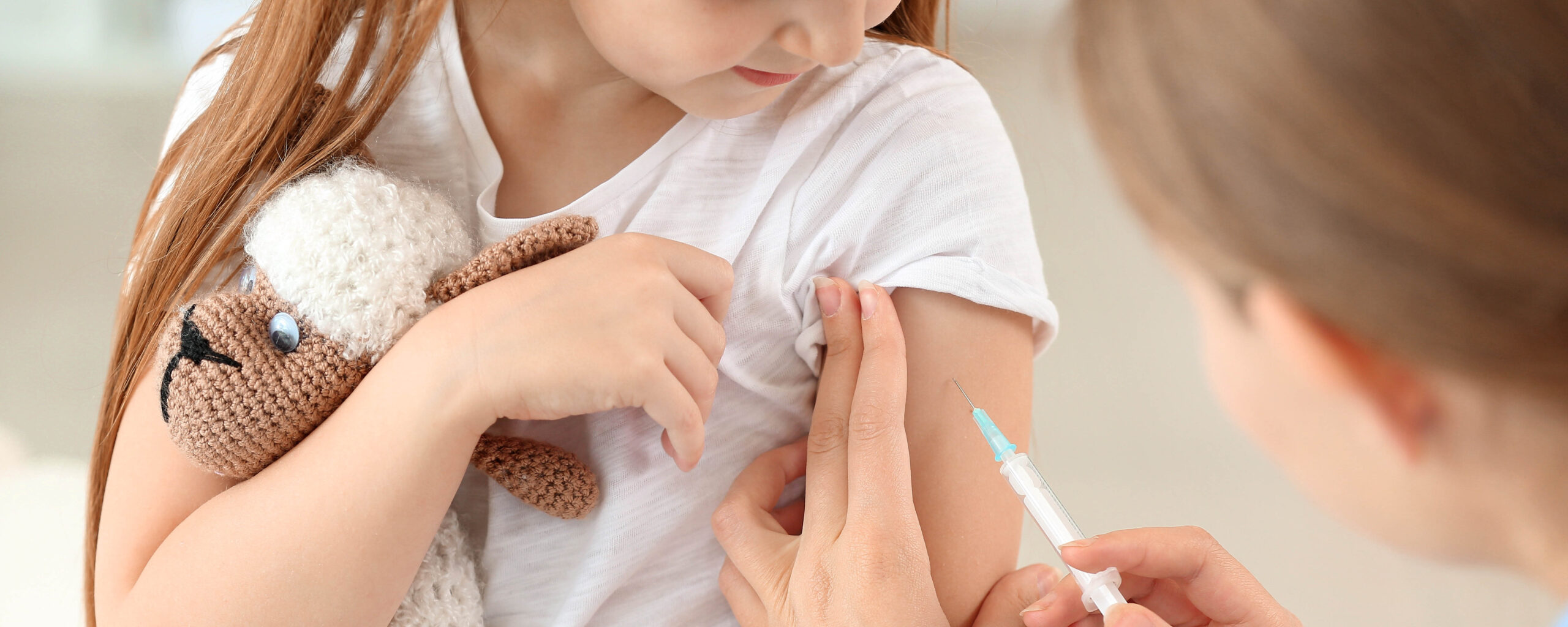
An APPC survey finds public support of the MMR vaccine has declined since November 2024, and the public is confused about whether HHS Secretary RFK Jr. recommends the MMR vaccine.
APPC survey reveals a reluctance among the public to recommend that someone who is pregnant receive certain routine vaccinations.
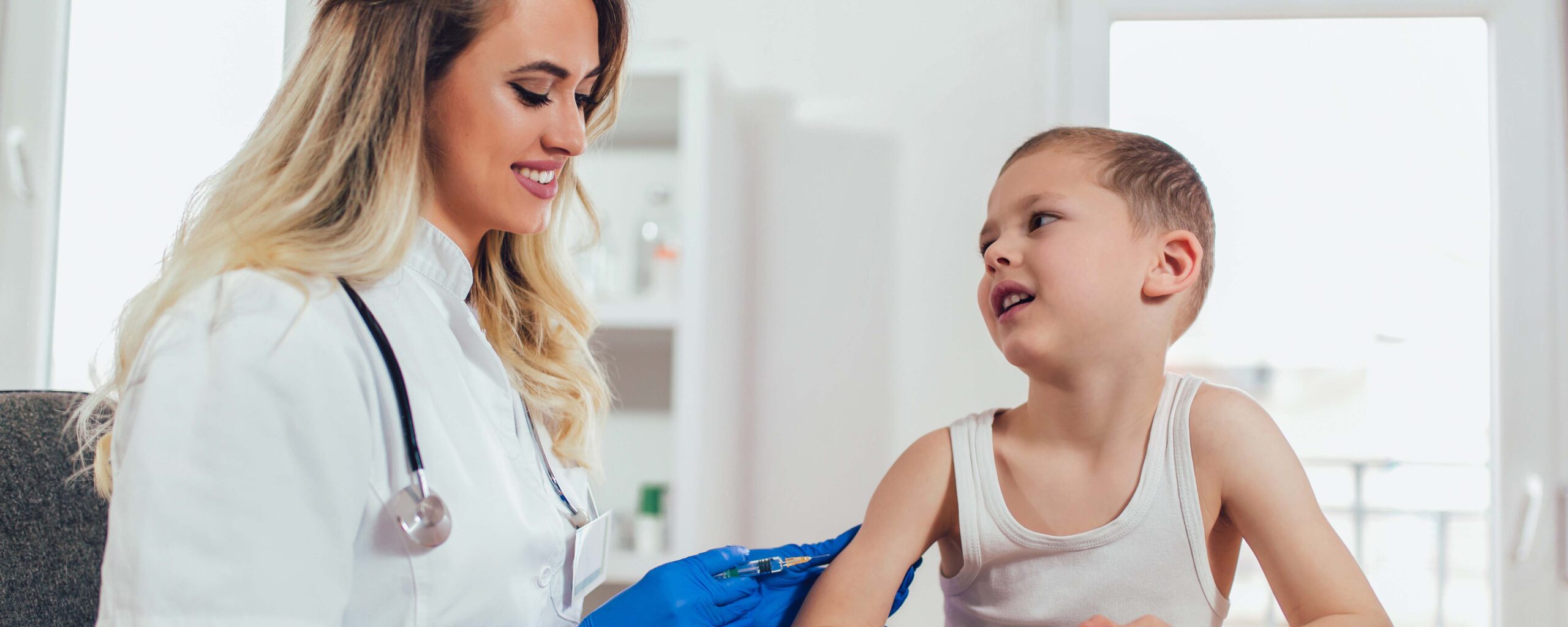

A 2025 Annenberg survey found that 70% of U.S. adults support an MMR vaccine requirement for healthy children to attend public school.

According to a new Annenberg Public Policy Center survey, most people are uncertain about which vaccinations are safe and recommended for pregnant people.

Amid a significant U.S. measles outbreak, a new APPC survey finds that many Americans do not understand the potential severity of the disease.
APPC and CHOP's Vaccine Education Center produced a video showing why it is virtually impossible for foreign DNA fragments to damage our own DNA.
A paper reviewing APPC research during the pandemic finds a "conspiracy mindset" was a major factor in resistance to Covid vaccination.

We've compiled a list of essential FactCheck.org reads about Secretary of Health and Human Services nominee Robert F. Kennedy Jr. and his remarks about vaccines, autism, Covid-19 and other topics.

Most U.S. adults support school vaccination requirements and policies requiring children to be vaccinated against preventable diseases such as measles, mumps, and rubella, an APPC study finds.